WiFi transmissions are essentially radio waves, similar to the electromagnetic waves produced by your mobile phone or radio. However, unlike electromagnetic waves, WiFi signals are concise. They are usually only twelve centimeters long compared to AM waves, which are hundreds of meters long. The signal weakens as it gets further away from the source, and it cannot generally get more than a hundred and fifty feet away from a source.
Because WiFi signals are absorbed and obstructed by walls, and metallic objects, the WiFi router antenna position significantly impacts WiFi router speed and signal strength throughout your home.
In general, the antenna position should be pointed vertically out of the sensor and aligned in the same direction. Install the sensor flat on its back on a horizontal surface, and bend the antenna as near to the sensor housing as possible to get the antenna pointing vertically.
This article outlines the most popular methods for positioning WiFi antennas and determining the best location for you. We will also present the best way to maximize the performance of your WiFi router.
How to Position WiFi Antennas in 3-Easy Steps

Most people consider router aspects such as speed, power, and WiFi protocols, but WiFi antenna location is also essential. Here’s how to place router antennas for optimal performance. (1)
The basic strategy follows a pattern that works on WiFi router antenna position in most cases.
Step 1: If your WiFi router has feet, place it on them rather than on its side. If the router has no feet on both sides, you can select any position.
Step 2: Locate the access point antennas on your router. If you cannot locate any external antenna, your router has internal access point antennas.
Step 3: If you only need coverage for one floor, place some vertically and some horizontally.

Manufacturers usually recommend that all antennas point straight up, but WiFi works best when the router and device antennas are positioned in the same direction. Laptop antennas are typically horizontal, but phone and tablet antenna locations vary.
Alternative Way Positioning Router Antennas
Since every WiFi arrangement is different, you’ll need to conduct some testing to get the maximum performance out of your router. To begin, you’ll need a way to monitor the signal strength on your computer, tablet, or phone.
Once you’ve established a method for recording signal strength, you may experiment with different antenna placements.
Step 1: After initial setup, check the strength of your WiFi signal at several locations around your service area. Begin using the manufacturer’s suggested antenna placement.
Step 2: Take note of the signal strength and speed in different areas of your service area.
Step 3: Realign your antennas and test again until you’ve found the best configuration.
Position Your WiFi Router for Best Reception and Performance
Step 1: Put your WiFi router in a prominent area
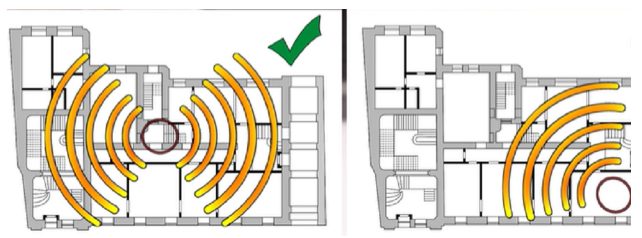
Since the router significantly influences network speed, keep it as near to the middle of the room as possible.
Step 2: Place your WiFi router at a specific height
It is preferable to position the wireless router on a table or shelf at a specific height to extend the directional antenna’s transmitting capabilities. (2)
Step 3: Avoid using high-powered appliances
When the router transmits signals, high-power electrical appliances and iron items may cause WiFi interference.
Step 4: Avoid barriers
Many people put the router in a cabinet to keep it visually pleasing. Putting it in the cabinet will obstruct the signal and degrade the overall movement. The more the interference and the poorer your connection, the closer your wireless router is to these obstructions.
Step 5: Avoid overexposure
Keep the router in as cool a place as possible. Because long-term sun exposure will cause harm to the router, affecting network stability and speed.
Take a look at some of our related articles below.
- Test TV signal strength
- What direction to point outdoor TV antenna
- Multi-directional vs Omnidirectional antenna
References
(1) WiFi protocols – https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/
articles/000005725/wireless/legacy-intel-wireless-products.html
(2) router – https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/small-business/resource-center/networking/types-of-routers.html

